WHAT IS ALPHA-LACTALBUMIN?

Also known as alpha, alpha-lac, or lactalbumin, alpha-lactalbumin is one of the main protein fractions naturally occurring in milk. Alpha is the most prominent protein fraction in human milk and second most prominent fraction in bovine milk. It is naturally high in the essential amino acid tryptophan, and the sulphur amino-acid, cysteine.
What are alpha-lactalbumin’s benefits and what are the mechanisms?
INFANT NUTRITION
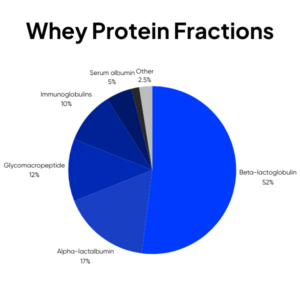
One of the key features of alpha-lactalbumin is its amino acid profile, which includes a relatively high tryptophan and cysteine content. The level of these amino acids in cow’s milk is around half that in human milk; however, bovine alpha-lactalbumin has a higher level of these key amino acids, thus can allow amino acid profiling of formula much closer to human milk (figure below).
Mother’s milk needs to provide all the essential amino acids for the infant’s growth and if not breastfed, the alternative nutritional source must provide these. The difference in amino acid content of human vs cow’s milk leads to the higher protein content of infant formulas, to ensure sufficient amino acid intake. Tryptophan and cysteine are key, as the level of both amino acids in cow’s milk is around half that in human milk; however, using alpha-lactalbumin compensates for this and allows amino acid profiling of formula closer to human milk.
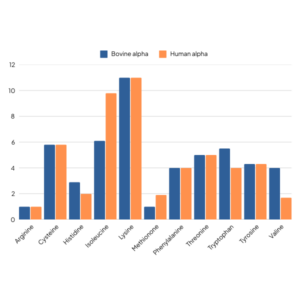
However, the amino acid needs cannot be solely met by using alpha as the only whey fraction in formula. Given the low arginine content of alpha-lac, this would leave to suboptimal intake, so a combination alpha, alongside a reduced β-lactoglobulin, and careful selection of other proteins will provide optimal composition.
Formulas rich in alpha-lac have been shown to be beneficial for gastrointestinal health of the infant; preventing E-coli induced diarrhoea and providing a bifidogenic effect for enhanced gastrointestinal comfort and development.
ADULT NUTRITION
Tryptophan is the precursor of serotonin, which is a neurotransmitter and functions as the precursor to melatonin (hormone involved in the sleep-wake cycle). Serotonin exerts multiple effects and is popularly thought to be a main contributor to feelings of well-being and happiness. It is implicated in the following:
- Mood
- Cognitive performance
- Sleep regulation
- Weight management
Serotonin Synthesis
Serotonin is synthesized from tryptophan (TRP) and brain serotonin concentrations rise with tryptophan intake (Markus et al, 2000). Additionally, it is important the ratio between tryptophan and large neutral amino acids (LNAA) is high, as they both use the same amino acid transporter across the blood brain barrier (figure below). (Other ways to manipulate TRP uptake include increasing carbohydrates, as the associated insulin response then encourages uptake of LNAAs in the muscle tissue, thus favourably altering the plasma TRP:LNAA).
Is there clinical evidence supporting alpha-lactalbumin’s benefits?
Alpha-lac has long been studied and has a large body of evidence behind its benefits.
Mood
As little as 500mg has been shown to enhance the plasma TRP:LNAA levels by 48% against placebo, in both low- and high-stress vulnerable subjects (figure 6 – Markus et al, 2000).
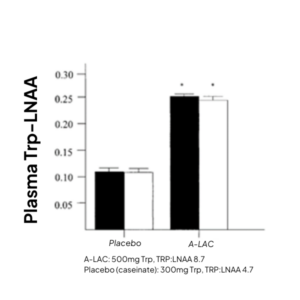
Figure 6. Plasma TRP:LNAA for both low and high stress vulnerable groups
A decline in serotonin activity in the brain is involved in the development of depressive mood, whereas increased brain serotonin may help improve the ability to cope with stress.
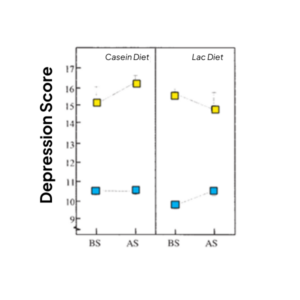
In the same study as above, Markus et al investigated the impact of the drinks on depression scores. The supplements were given in 2 drinks – one at breakfast, one at lunch – and the subject underwent experimental stress in the afternoon. In high stress-vulnerable individuals, there was a reduction in depression scores.
Change in depression scores before(BS) and after stress (AS) tests in high stress vulnerable and low stress vulnerable subjects. Split into casein and alpha-lac diet
Cognitive Performance
Cognitive performance often declines during exposure of chronic stress. The negative effect of chronic stress may be mediated by reduced brain serotonin function. Thus, a diet-induced increase in the serotonin precursor tryptophan help increase brain serotonergic activity levels and improve cognitive performance. Studies have shown benefits of alpha supplementation on cognitive performance, including:
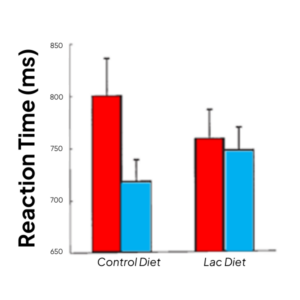
- Faster reaction time with 500mg TRP from alpha compared to 300mg TRP from caseinate, in high stress vulnerable adults (Markus et al, 2002)
- Improved memory after consumption of an alpha-lactalbumin diet compared to a caseinate diet
Enhanced Sleep – Overnight Recovery
Benefits on sleep quality have been observed from both alpha supplementation and tryptophan supplementation. These include:
- In those with mild sleep complaints, alpha-lac (providing 1.9g TRP) was found to reduce morning sleepiness score, implying a better night’s sleep (Markus et al 2005)
- Reduce sleep latency (time to get to sleep) in those who normally have a longer sleep latency, with 1g TRP supplementation
Pre-bed protein feeding is generally recognised to enhance muscle resynthesise and growth, and while most work has been done using casein, there is no reason to believe whey protein would not be just as effective (Trommelen and Loon, 2016)
Weight Management
Although the effects of dietary protein and whey proteins are well known, studies comparing different protein types or fractions are scarce. However, it has been demonstrated that alpha-lactalbumin has an increased effect on satiety compared to other protein sources such as WPI and it is down to more than just the TRP (Nieuwenhuizen 2008; Pilvi et al, 2009; Veldhorst et al 2008). More work is required in this area.
What applications does alpha-lactalbumin work in?
Alpha-lactalbumin works well across applications. RTM powdered shakes, RTD ready-to-drink, bars, cookies and many more.